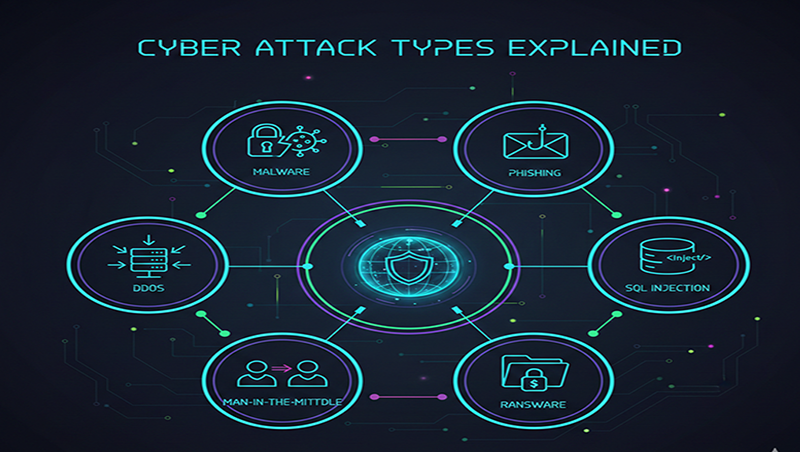
Cyber Attack Types Explained
Cyber
attacks are deliberate attempts by threat actors to breach, disrupt, or damage
computer systems and networks. In 2026, these attacks are becoming increasingly
sophisticated, frequently leveraging AI to scale operations and bypass
traditional defenses.
Most
Common Cyber Attack Types (2026)
- Malware: An umbrella term for
malicious software designed to damage or gain unauthorized access to a
system.
- Ransomware: Encrypts a victim's files
and demands a ransom, typically in cryptocurrency, for the decryption
key.
- Trojans: Disguises itself as
legitimate software to create "backdoors" for attackers.
- Spyware: Secretly monitors user
activity to steal credentials or sensitive data.
- Phishing & Social
Engineering: Attacks
that exploit human trust rather than technical flaws to steal information.
- Phishing: Fraudulent messages
(emails, texts, calls) that trick users into revealing data or clicking
malicious links.
- Spear Phishing: Highly targeted phishing
aimed at a specific individual or organization.
- Whaling: Spear phishing that
specifically targets high-level executives (C-suite).
- Business Email Compromise
(BEC): Impersonating
a trusted business associate to trick employees into unauthorized fund
transfers.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) and
DDoS: Overwhelming
a system with traffic to make it unavailable to legitimate users.
Distributed DoS (DDoS) uses a network of compromised devices, known as
a Botnet, to launch the attack.
- Injection Attacks: Exploiting vulnerabilities
to input malicious code directly into an application.
- SQL Injection (SQLi): Inserting malicious SQL
commands into a database to steal or delete records.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): Injecting scripts into a
legitimate website that run in the browsers of visiting users to steal
session data.
- Man-in-the-Middle (MitM): Intercepting and
potentially altering communications between two parties without their
knowledge, often occurring on unsecured public Wi-Fi.
- Zero-Day Exploits: Attacks that target
previously unknown software vulnerabilities before developers have a
chance to release a patch.
- Supply Chain Attacks: Targeting a company's
software vendors or service providers to gain an indirect path into
multiple organizations.
- Cryptojacking: Unauthorized use of a
victim's computing resources to mine cryptocurrency.
Emerging
Threats in 2026
- AI-Powered Attacks: Use of generative AI to
create hyper-realistic deepfakes, automate phishing, and develop malware
that can adapt to defenses in real-time.
- Fileless Attacks: Malware that resides only
in a computer's RAM rather than on the hard drive, making it extremely
difficult for traditional antivirus software to detect.
- IoT Attacks: Exploiting vulnerabilities
in connected "smart" devices (cameras, thermostats, industrial
controls) to launch broader network attacks.