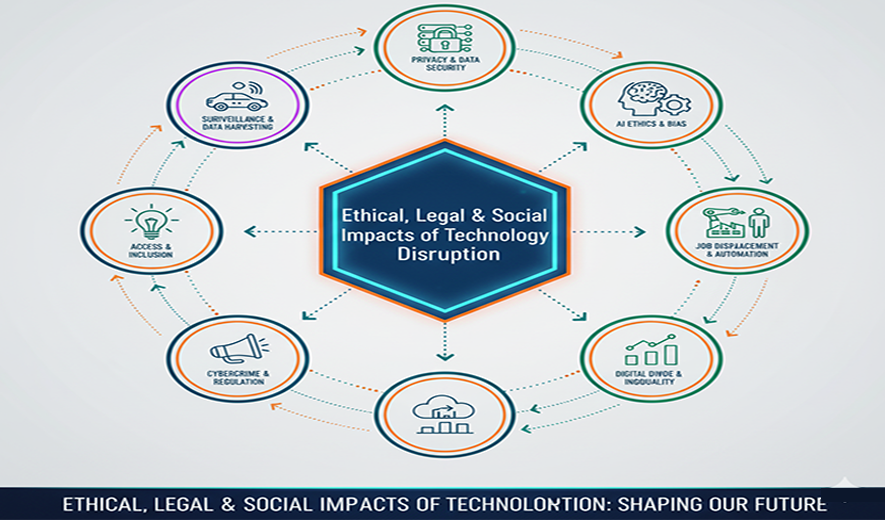
Ethical, Legal & Social Impacts of Technology Disruption
Technological disruption creates significant ethical, legal, and social impacts by upending established norms and systems. While technologies offer progress and efficiency, they also introduce complex challenges that governments, businesses, and individuals must navigate responsibly.
Bias and discrimination
Many AI and machine learning tools are trained on historical data, which can contain inherent human biases. If left uncorrected, these systems can unintentionally perpetuate or even amplify existing societal prejudices based on race, gender, or socioeconomic status.
- Case study: Amazon's AI hiring tool was found to be biased against women because it was trained on historical resume data that favored male candidates for technical roles.
Privacy and security
Digital technologies collect vast amounts of personal data, creating the potential for misuse, data breaches, and a loss of personal autonomy. Companies and governments face the ethical challenge of protecting this information while also using it for innovation.
- Case study: The Cambridge Analytica scandal revealed that Facebook user data was harvested without consent and used for political advertising, demonstrating how personal data can be misused for political agendas.
- Accountability and transparency
As AI systems make more critical decisions in areas like healthcare, finance, and criminal justice, determining who is responsible when things go wrong becomes difficult. The "black box" nature of some AI makes it challenging to understand how decisions are reached, obscuring accountability.
Manipulation and misinformation
Social media and AI can be used to spread misinformation and deepfakes, which can manipulate public opinion, undermine democratic processes, and cause reputational harm. The proliferation of online content without traditional editorial oversight has shifted what people perceive as trustworthy.
Legal impacts
Redefining intellectual property
The creation of content by AI challenges existing copyright and patent laws. Legal frameworks are struggling to determine whether AI-generated works can be protected by copyright and who the owner is—the AI, the programmer, or the user.
Liability for autonomous systems
Legal systems are being tested by technologies like self-driving cars. If an autonomous vehicle causes an accident, legal responsibility is unclear. Potential liable parties could include the manufacturer, the software developer, the car's owner, or the AI itself, prompting the need for entirely new regulatory frameworks.
Data protection and regulation
The increase in data collection has led to new laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe. These regulations aim to give individuals more control over their data, but they require continuous adaptation as technology evolves.
Cybersecurity and cybercrime
Cybercrime is a rapidly growing area of criminal activity that poses a significant threat to critical infrastructure and personal data. As new technology provides more ways for bad actors to cause harm, legal systems must find ways to police the digital world and enforce security measures.
