Digital Twins & Simulation in Manufacturing / Logistics
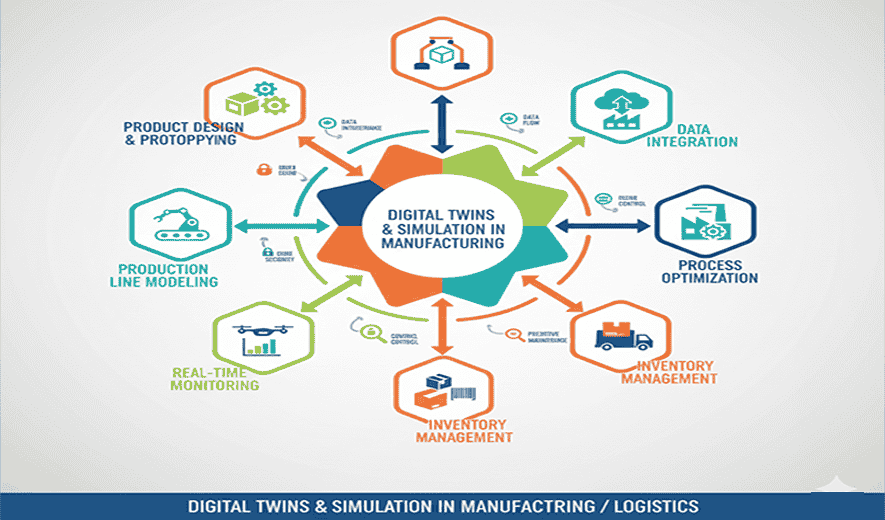
Digital twins are virtual, real-time replicas of a physical object, system, or process that are used to monitor, analyze, and simulate its real-world performance. In manufacturing and logistics, they are combined with simulation to optimize operations, reduce costs, and build greater resilience against disruptions.
How digital twins and simulation transform manufacturing
Design, planning, and optimization
- Virtual prototyping: Manufacturers create a digital twin of a product to simulate its performance under various conditions, such as stress or heat. This reduces the need for expensive physical prototypes and speeds up the design cycle.
- Factory layout optimization: Before any physical changes are made, a production twin can be used to test different layouts for machinery and production lines. This identifies the most efficient configuration, minimizes waste, and optimizes workflows.
- Risk assessment: Simulation allows manufacturers to create a "sandbox" environment to test how a new process will work before rolling it out. This allows for risk assessment and the prevention of costly, disruptive mistakes.
Predictive maintenance and quality control
- Predictive maintenance: Sensors on a machine constantly feed real-time performance data (e.g., temperature, vibration) to its digital twin. AI and machine learning analyze this data to predict when a component is likely to fail, enabling maintenance to be scheduled proactively and reducing unplanned downtime.
- Quality control: By monitoring the manufacturing process in real-time, digital twins can detect anomalies and quality issues as they arise. This allows for immediate corrections, reducing the number of defective products and minimizing waste.
Real-world examples in manufacturing
- BMW's iFactory: The automaker created a digital twin of all 31 of its production sites to reduce production planning times by nearly a third. This allows plant designers to create more efficient layouts and processes virtually, with thousands of employees able to "walk through" the factory in real-time from anywhere in the world.
- Tesla's EV production: Tesla uses digital twins throughout its electric vehicle manufacturing process to simulate and monitor everything from battery performance to the efficiency of the powertrain. This allows engineers to test and refine products virtually, resulting in faster production and higher quality.
