DevOps Culture: Roles & Practices
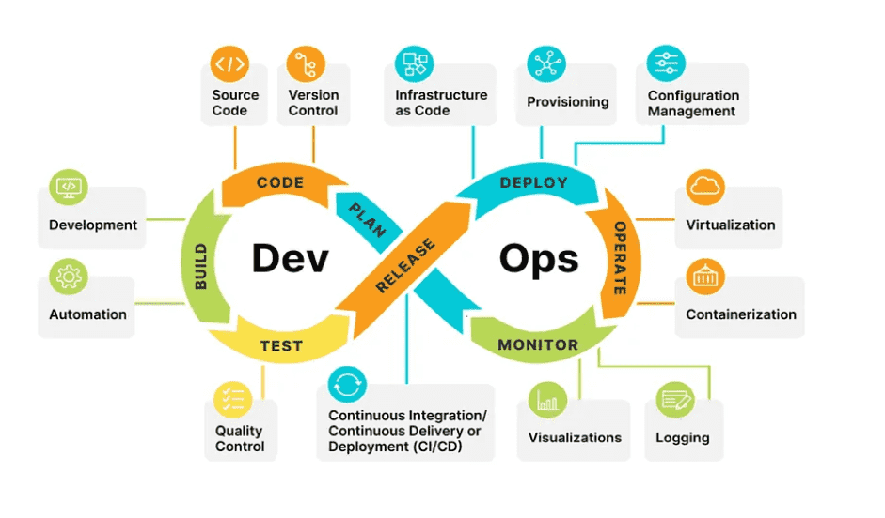
DevOps is a cultural and technical philosophy that aims to integrate software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops) to accelerate and improve the software delivery lifecycle. It breaks down the traditional silos between these teams by promoting collaboration, automation, and shared responsibility. A strong DevOps culture enables organizations to produce higher-quality, more reliable software, adapt quickly to market demands, and increase customer satisfaction.
The core culture of DevOps
The fundamental principles that define a DevOps culture are often summarized by the acronym CALMS:
- Culture: This is a mindset shift that promotes trust, communication, and collaboration across all teams involved in software delivery. Teams move away from a "throw it over the wall" mentality to one of shared ownership and shared goals. A key aspect is the adoption of "blameless retrospectives," which focus on learning from incidents and improving processes rather than finding fault with individuals.
- Automation: Automation is central to DevOps, and the mantra is "automate everything". This includes every stage of the software delivery process, from testing and deployment to infrastructure provisioning and configuration management. Automation reduces manual errors, increases efficiency, and makes processes reliable and repeatable.
- Lean: Lean principles focus on maximizing value for the customer by eliminating waste and streamlining processes. This involves working in small batches, reducing cycle times, and continuously measuring and improving workflows.
- Measurement: DevOps teams collect and analyze data across the entire software delivery lifecycle, including performance metrics, customer feedback, and incident response times. This data-driven approach allows for informed decision-making and helps identify areas for continuous improvement.
- Sharing: A culture of sharing information, knowledge, and feedback is vital for continuous learning. Open communication, shared dashboards, and collective problem-solving ensure that everyone is aligned and empowered to improve the product and process.
Common DevOps roles
While DevOps is a shared responsibility, certain roles have emerged to facilitate and drive these practices.
- DevOps Engineer: This is often a bridge role, advocating for and implementing DevOps practices across an organization. Responsibilities include building and maintaining CI/CD pipelines, managing infrastructure, and automating workflows.
- DevOps Evangelist: This person is a leader who champions the cultural transformation needed for DevOps adoption. They articulate the benefits of DevOps to secure buy-in from all teams and empower individuals to make changes.
- Release Manager: In a DevOps environment, release managers oversee the coordination and scheduling of software releases, working to ensure a smooth, automated process.
- Software Developer: Developers in a DevOps culture are more involved in the entire software lifecycle. This includes being involved in planning, testing, and monitoring their application in production.
- Site Reliability Engineer (SRE): An SRE is focused on the reliability, availability, and performance of a system. SRE is a specific implementation of DevOps principles that uses software engineering practices to solve operational problems.
- Security Engineer (DevSecOps): With the rise of DevSecOps, security engineers are integrated into the DevOps process from the beginning. They focus on automating security checks and building a secure-by-design pipeline.
