Future of ERP: Trends, AI-driven Insights, etc.
The future of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is being shaped by artificial intelligence (AI), cloud technology, and a move toward modular, flexible systems. Instead of being static systems for back-office functions, ERPs are evolving into strategic, proactive platforms that drive business growth and agility.
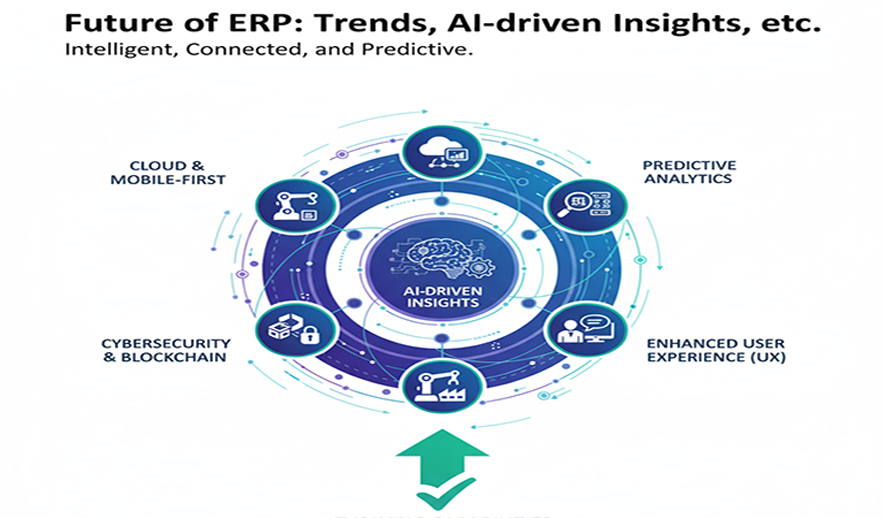
AI and machine learning (ML)
AI and ML are transforming ERP systems from data repositories into intelligent tools that automate, predict, and optimize performance across the organization.
- Generative AI: Beyond simple automation, generative AI can create detailed business reports, draft marketing content, and generate various business scenarios for strategic planning.
- Agentic AI: Autonomous AI agents are being deployed to handle complex tasks with minimal human intervention, automating decision-making in real-time.
- Predictive analytics: AI-driven ERPs use predictive analytics to forecast demand, predict cash flow, identify potential supply chain disruptions, and flag potential fraud with higher accuracy.
- Intelligent automation: Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and ML are automating routine and repetitive tasks like invoice processing, data entry, and payroll, freeing up employees for higher-value, strategic work.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP is simplifying user interaction by allowing employees to use voice or text commands to query the system and receive instant, conversational responses.
Composable and modular ERP
The traditional, monolithic ERP model is being replaced by a more adaptable and flexible approach that allows companies to build and modify their systems as needed.
- Composable ERP: This approach allows businesses to assemble independent, interoperable modules or microservices from different vendors based on specific business needs.
- Modular architecture: Organizations can start with core functions and add or replace modules over time without overhauling the entire system. This allows for easier and faster integration of emerging technologies.
- Two-tier ERP: Large enterprises are adopting a two-tier strategy, using a centralized ERP for corporate functions (tier 1) while allowing subsidiaries and individual business units to operate on more agile, local systems (tier 2).
