Cloud vs On-Premise ERP Solutions
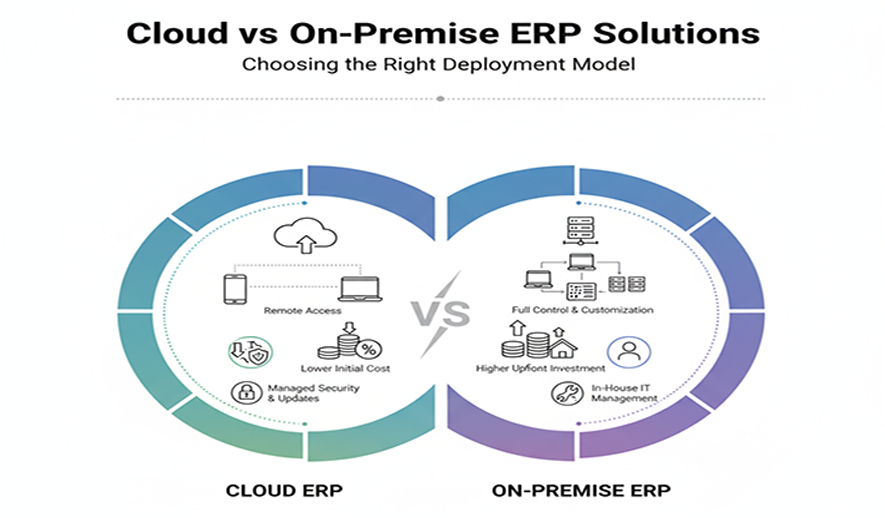
Cloud ERP
- Lower Initial Cost: Cloud ERP uses a subscription-based (SaaS) model, reducing the need for large upfront investments in hardware and licenses.
- Faster Deployment: Implementation is quicker, often taking months instead of years, since the vendor manages the infrastructure.
- Reduced IT Burden: The vendor handles software maintenance, upgrades, and system upkeep, freeing up your internal IT team.
- Accessibility: Users can access the system from anywhere with an internet connection, supporting remote work and multiple locations.
- Scalability: You can easily add or remove users and resources to match your business needs without complex infrastructure changes.
- Automated Updates: The vendor automatically applies updates, ensuring you always have the latest version with current security features.
- Enhanced Security: Reputable cloud providers invest heavily in robust security measures, disaster recovery, and data backups.
- Internet Dependency: A stable internet connection is required for access, and a network failure could interrupt operations.
- Limited Customization: Solutions are often standardized, which can limit the ability to tailor the software to highly unique or complex workflows.
On-Premise ERP
- Higher Upfront Investment: Requires a significant initial capital investment in hardware, perpetual software licenses, and IT infrastructure.
- Complete Data Control: The software and data are hosted on your own servers, giving you full control over security and data residency.
- Full Customization: Offers greater flexibility for extensive customization, allowing you to tailor the software to your specific business processes.
- No Internet Dependency: The system's performance is not dependent on external network connectivity.
- Slower Deployment: The implementation is typically a longer, more complex process due to hardware setup and extensive configuration.
- Higher IT Burden: Your company is responsible for all system maintenance, security, and updates, which requires a dedicated IT team.
- Limited Scalability: Scaling requires significant and often costly investments in additional hardware.
- Access Limitations: Remote access can be challenging and may require additional security measures.
