Static vs Dynamic Websites: Decision Guide
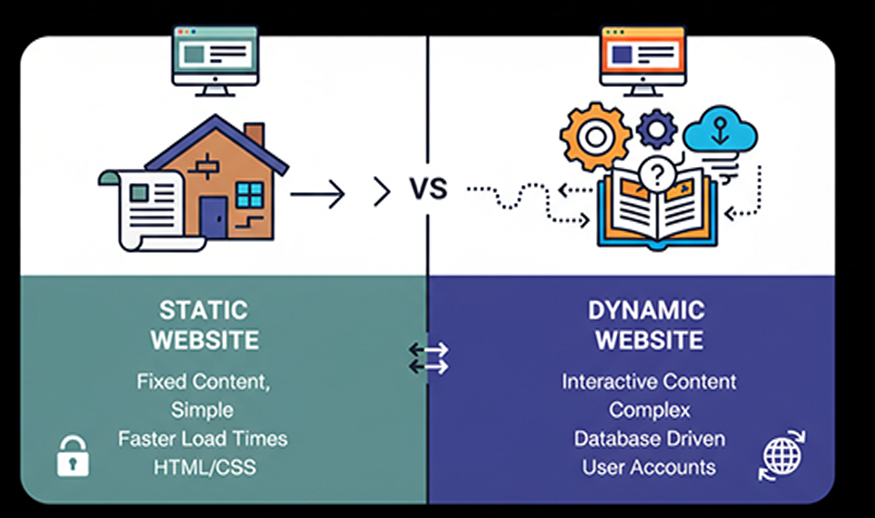
static website serves the same fixed content to every visitor, while a dynamic website generates content in real-time based on user actions and other variables. Your choice depends on your budget, need for customization, and how often your content changes.
Static websites
Static websites are simpler and ideal for informational sites that rarely change.
Pros
- Fast performance: Since pages are pre-built, they load quickly for users, which helps with search engine rankings.
- High security: There is less risk of hacking because there is no database or server-side scripting to exploit.
- Cost-effective: Development is faster, hosting is cheaper, and maintenance costs are lower.
- Reliable: With fewer complex components, they are less likely to experience technical issues.
Cons
- Difficult to update: Making changes requires manually editing the site's code, which can be time-consuming for large sites.
- Limited functionality: They lack advanced features like user accounts, shopping carts, and real-time updates.
- Poor scalability: Managing a large number of pages and making site-wide changes can be cumbersome.
Dynamic websites
Dynamic websites are more complex, offering personalized and interactive user experiences.
Pros
- Interactive and personalized: Content can be tailored based on user behavior, location, or past actions.
- Easy content management: A Content Management System (CMS), like WordPress, allows non-technical users to update and add content easily.
- Highly scalable: Adding new features and managing content is straightforward, making them great for growing businesses.
- Advanced functionality: They support complex features like e-commerce stores, user accounts, and integrated applications.
Cons
- Higher costs: They are more expensive to develop and maintain due to complex infrastructure, hosting needs, and regular updates.
- Slower performance: Pages can load slower because they are generated in real-time. This can be mitigated with caching and CDNs.
- Increased security risks: Interactions with databases and user input create more opportunities for security threats.
