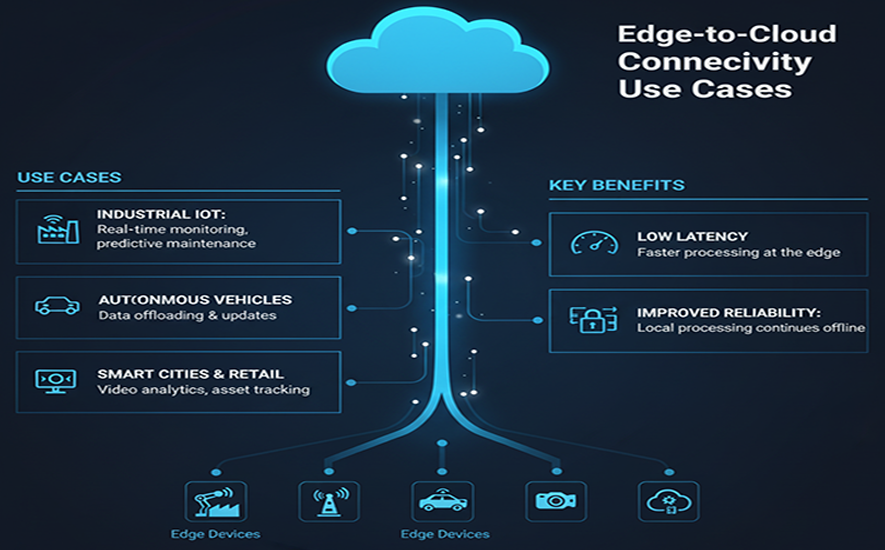
Edge-to-Cloud Connectivity Use Cases
Edge-to-cloud connectivity enables hybrid computing models where data processing and analysis are distributed between local 'edge' devices and centralized 'cloud' services. The optimal distribution of tasks is based on factors like latency requirements, bandwidth constraints, and the need for large-scale aggregation or model training.
1. Industrial Internet of Things and Smart Manufacturing
Edge-to-cloud is crucial in factories and industrial plants for real-time control and long-term optimization.
- Predictive Maintenance: Edge devices (sensors, gateways) perform real-time analysis of machine vibration, temperature, and performance data to immediately detect anomalies. This ultra-low latency processing triggers local alerts or automatic shutdowns. The filtered data is then sent to the cloud for long-term storage, fleet-wide analysis, and training of improved predictive models that can be deployed back to the edge.
- Process Optimization and Control: Edge computing handles closed-loop control of assembly lines, robotics, and quality checks where milliseconds matter. The cloud provides centralized orchestration and reporting across multiple plants for macro-level efficiency improvements and resource management.
2. Autonomous Systems and Transportation
Applications that require split-second decision-making rely heavily on edge processing, while the cloud supports overall learning and management.
- Autonomous Vehicles: The vehicle's on-board edge computer processes sensor data (LiDAR, cameras, radar) in real-time to make immediate navigation and safety decisions (e.g., braking, steering). Only aggregated, non-time-critical data, or specific event footage is transferred to the cloud for AI model retraining, map updates, and fleet management.
- Traffic Management in Smart Cities: Edge devices at intersections process video and sensor data to adjust traffic signals in real-time for optimal flow. The cloud aggregates data from the entire city to identify long-term traffic patterns, optimize public transport routes, and deploy complex, network-wide traffic policies.
3. Healthcare and Remote Patient Monitoring
Combining local privacy with central expertise is a key advantage in healthcare.
- In-Hospital Patient Monitoring: Edge devices/servers in a hospital perform real-time analysis of vital signs from patient monitors. This local processing ensures immediate alerts to staff and complies with data privacy/sovereignty regulations (like keeping patient data within the hospital network). The cloud is used for anonymized data aggregation for medical research, drug trial analysis, and large-scale diagnostics model development.
- Wearable Health Devices: A wearable device uses edge processing to continuously monitor and immediately alert a user to a critical event (e.g., a severe fall or irregular heart rhythm). Aggregated, non-critical health metrics are securely uploaded to the cloud for a doctor's remote patient monitoring and long-term health trend analysis.
4. Retail and Customer Experience
Edge-to-cloud enhances in-store operations with localized and centralized intelligence.
- In-Store Analytics: Cameras and sensors at the edge of a store process video in real-time to identify stock levels, customer queues, and foot traffic. This local analysis protects customer privacy by not sending raw video to the cloud. Key insights and sales data are sent to the cloud for inventory management, cross-store comparison, and centralized merchandising strategy.
- Smart Point of Sale (POS) and Kiosks: Edge devices run POS applications locally for offline resilience (processing payments even if the internet is down). Transaction data is synchronized with the cloud once connectivity is restored for accounting, inventory updates, and fraud detection across the enterprise.
5. Telecommunications
The combination enables the new low-latency services required by 5G networks.
- Virtualised Radio Access Network: Edge computing is used at the base station to run the virtualized network functions that require ultra-low latency for 5G services. The cloud provides centralized management, orchestration, and scaling of the infrastructure across the entire mobile network.
