Prioritize Cloud Security
To prioritize cloud security, apply best practices for data encryption, Identity and Access Management (IAM), and compliance. Strong cloud security is a shared responsibility between the cloud provider and the customer.
Best practices for data encryption
Data encryption makes your data unreadable to unauthorized users, protecting sensitive information even if other security layers are compromised.
-
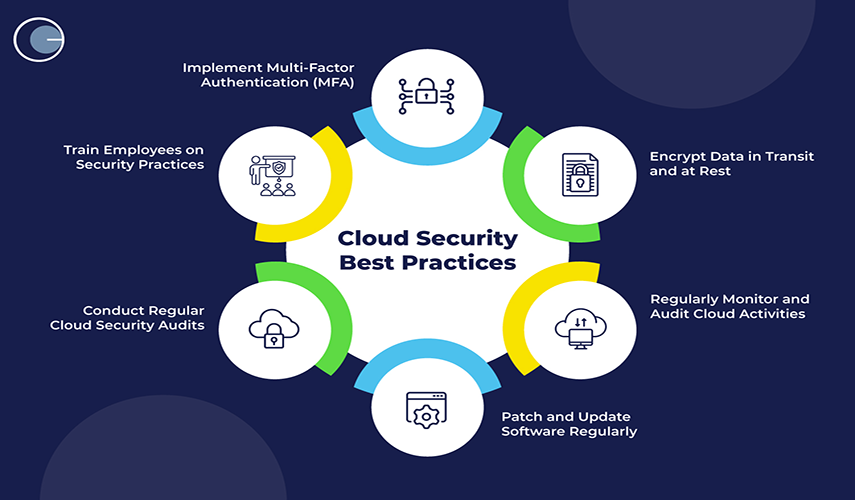
Encrypt data in all states: Encrypt data when it is stored ("at rest"), when it is moved across networks ("in transit"), and even when it is actively being processed ("in use").
- At Rest: Utilize cloud provider services like Amazon S3 bucket encryption, Azure Disk Encryption, or Google Cloud Storage encryption.
- In Transit: Secure data moving across networks using Transport Layer Security (TLS).
- In Use: Use confidential computing technologies to protect sensitive data while it is being processed.
- Manage your encryption keys securely: Use robust key management systems (KMS) offered by cloud providers, such as AWS KMS or Azure Key Vault, to manage the lifecycle of your encryption keys.
- Use strong, industry-standard algorithms: Employ powerful algorithms like AES-256 for data encryption.
- Encrypt client-side: For maximum control, encrypt sensitive data before uploading it to the cloud.
Best practices for Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Robust IAM policies control who can access cloud resources and what actions they can perform, enforcing the principle of least privilege.
- Enforce the principle of least privilege (PoLP): Grant users and services only the minimum permissions necessary to perform their required tasks. Regularly audit and revoke unused permissions.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA): Implement MFA for all users, especially for administrative accounts, to add an extra layer of security beyond just a password. Phishing-resistant MFA, like hardware-based tokens, is recommended for high-risk accounts.
- Automate user lifecycle management: Use automated workflows to provision and de-provision access for employees as they join, leave, or change roles. This helps prevent orphaned accounts and reduces administrative burden.
- Use role-based access control (RBAC): Group users into roles (e.g., developer, admin) and assign permissions to those roles rather than to individual users. This simplifies administration and access review.
- Monitor and audit IAM activity: Centralize logging of all IAM activities to detect suspicious behavior, track policy changes, and provide an audit trail for compliance.
- Secure privileged accounts: Implement Privileged Access Management (PAM) solutions to enforce strict controls, session monitoring, and frequent credential rotation for high-value accounts.
Best practices for compliance
Meeting regulatory requirements and industry standards is essential for protecting data and maintaining customer trust.
- Understand the Shared Responsibility Model: Recognize that compliance is a shared responsibility. While the cloud provider secures the underlying infrastructure, the customer is responsible for the security of their data, applications, and access control.
- Identify and understand relevant frameworks: Determine which regulations and frameworks apply to your organization (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, SOC 2, NIST) and establish policies that meet their requirements.
- Conduct regular audits and assessments: Perform routine security audits, vulnerability scans, and penetration tests to identify and address security gaps. These also help ensure continuous adherence to internal policies and external regulations.
- Automate compliance monitoring: Use cloud security tools, such as Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM), to continuously monitor your environment for misconfigurations and policy violations.
- Classify and govern data: Implement a data classification scheme to categorize data based on sensitivity. Establish and enforce governance policies to dictate how data is handled, stored, and accessed.
- Provide employee training: Regularly train all staff on security best practices, compliance requirements, and how to handle sensitive data responsibly to mitigate human error.
- Use cloud provider compliance tools: Leverage the compliance tools and resources offered by your cloud provider (e.g., AWS Config, Azure Policy, Google Cloud Security Command Center) to manage and automate compliance tasks.
