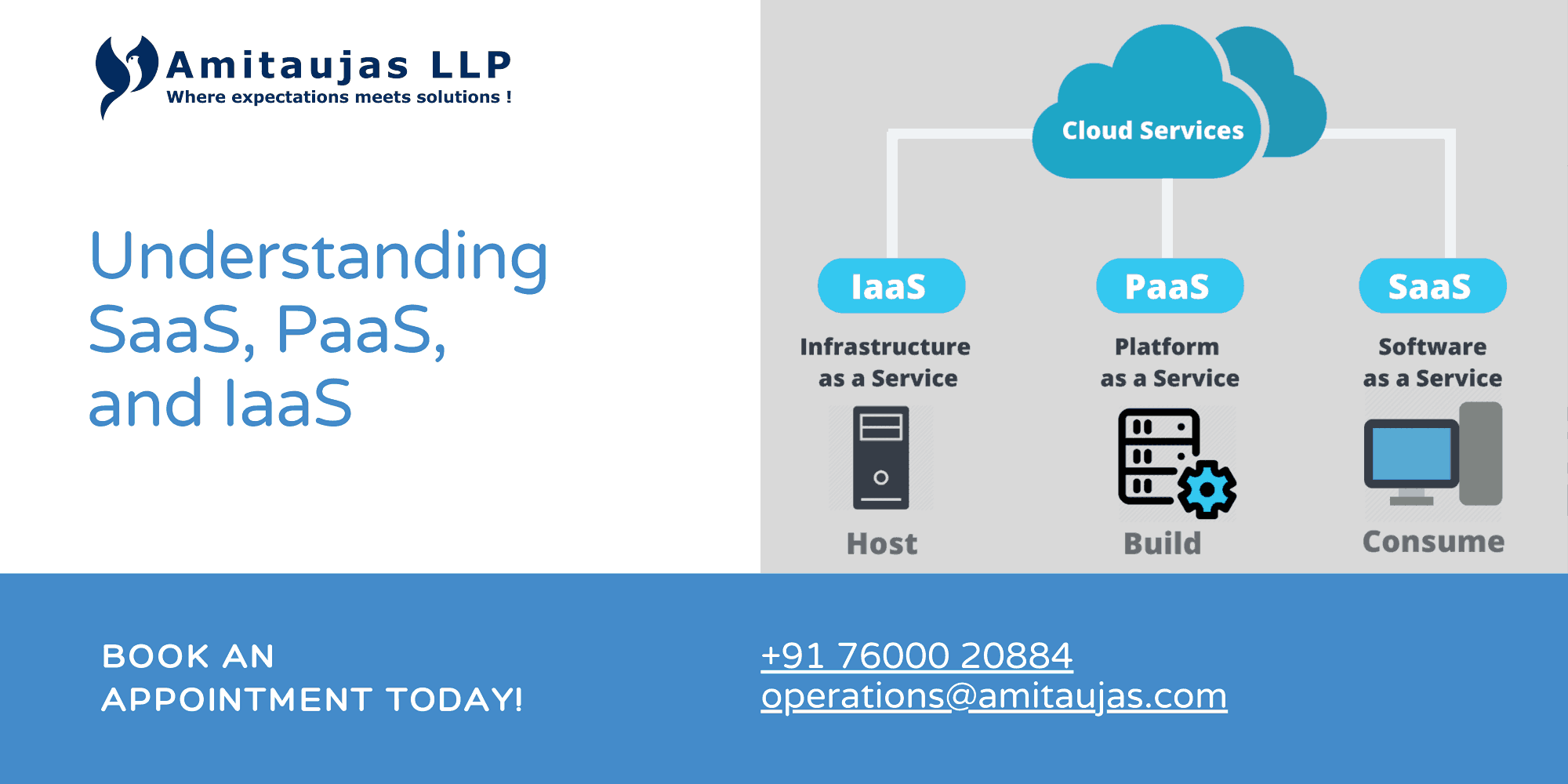
Understanding SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS
Understanding the different cloud computing service models—SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS—is important for businesses looking to make the most of cloud technologies. Here is an overview of each model:
1. Software as a Service (SaaS)
Definition: SaaS delivers software applications over the Internet on a subscription basis. Users access these applications through a web browser without installing or maintaining them on their devices.
Examples: Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, Salesforce, Slack.
Advantages:
- Access: Users can access applications from anywhere with an Internet connection.
- Automatic updates: Customers manage software updates and maintenance.
- Cost effective: Reduces the need for equipment and internal infrastructure.
- Good for: Businesses looking for turnkey applications without the need for extensive IT support.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Definition: PaaS provides a cloud-based platform that allows developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. It includes tools and services for development, testing, and deployment.
Examples: Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure App Services, Heroku.
Benefits:
- Simplified Development: Developers can focus on writing code instead of managing hardware and software infrastructure.
- Collaboration: Supports team collaboration with integrated development tools.
- Scalability: Scale applications as needed without managing the underlying infrastructure.
- Good for: Development teams looking for a robust environment to efficiently build and manage applications.
3. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Definition: IaaS provides virtual data resources over the Internet, such as servers, storage, and networks. Users can rent IT infrastructure and manage it as they wish.
Examples: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform.
Advantages:
- Flexibility and control: Users have full control over their infrastructure, which can be adapted to meet specific needs.
- Cost effective: Reduces the capital cost of physical equipment with a pay-as-you-go model.
- Increase: Increase or decrease resources as needed.
- Good for: Organizations that want to manage their own infrastructure but want to avoid the cost and complexity of physical hardware.
